Consider a use case where you want to query a PDF file. How can you do that? The simplest approach would be to copy all the content from the PDF and paste it into the input section of an LLM model (such as ChatGPT or Deepseek) before asking your question. However, this method fails if the PDF is very large or if you need to query multiple PDFs. The main limitation is the context window — the maximum number of tokens an LLM can process in a single query. Since context windows are limited, continuously asking questions in the same chat session will eventually lead to lower-quality responses and increased response times. Once the conversation exceeds this limit, the model starts "forgetting" earlier parts of the conversation, leading to lower-quality responses.
How Can RAG Help?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that enhances LLMs by combining retrieval-based methods with generative models, allowing them to reference external information beyond their training data.
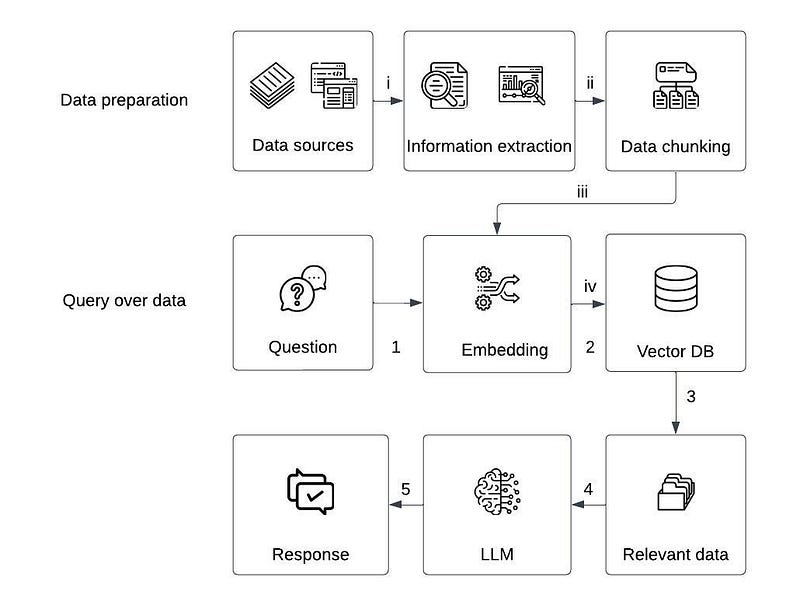
Data Preparation (Building the Knowledge Base)
Before querying, data needs to be preprocessed and stored efficiently.
- The system starts with data sources (e.g., PDFs, documents, structured data, web pages).
- Information is extracted from raw data using text processing tools, such as OCR (for PDFs), HTML parsers (for web data), or APIs.
- Extracted text is divided into smaller chunks (e.g., paragraphs, sections). This ensures that relevant parts can be retrieved instead of processing the entire document.
- The text chunks are converted into embeddings using an embedding model (like OpenAI's Ada, BERT, or SentenceTransformers). These embeddings are stored in a Vector Database (Vector DB) (e.g., FAISS, Pinecone, ChromaDB). A vector DB allows efficient similarity search to retrieve relevant content.
Query Processing (Retrieving & Generating Answers)
- The user inputs a question related to the stored data.
- The query is embedded into a vector representation using the same embedding model.
- The Vector DB performs a similarity search to find the most relevant chunks matching the question.
- The retrieved text chunks are passed as additional context to the LLM (e.g., GPT, Llama).
- The LLM combines retrieved data with its knowledge and generates a final response.
If you can see, In the naïve approach of directly prompting an LLM, we must provide the entire data source in the chat before asking a question. However, with RAG, we can store the information in a vector database and retrieve only the most relevant parts based on the query. This allows the LLM to generate responses using focused, relevant data instead of processing large amounts of unnecessary information.
By using retrieval instead of feeding the entire document into the model, RAG reduces token consumption, leading to lower inference costs and faster responses. This makes it more efficient than models with larger context windows, which can be computationally expensive.
